Miami, Florida – The International Society for Stem Cell Applications (ISSCA) is thrilled to announce the launch of its newest program, the Advanced Turkish Hair Transplant Certification. This pioneering training and certification initiative will take place from December 8th to 10th at the prestigious Cellular Hope Institute Facility in Cancun, Mexico. Physicians are encouraged to
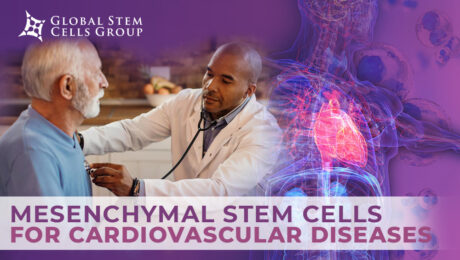
Despite progress in cardiovascular research, cardiac pathology continues to be one of the most common causes of morbidity and mortality in the world. Stem cell-based therapy has been recognized as an innovative strategy for the repair, regeneration and functional recovery of the myocardium, hence, once the animal research stage has been overcome, most clinical trials
Atherosclerosis is the most common form of arterial occlusive disease in adults. About 15 percent of adults over 55 years of age suffer from critical ischemia, the most severe form of this disease. Due to the gradual aging of the population and the growing number of people in their third age group, a number of
In recent years, MSCs have been introduced as respectable candidates for regenerative medicine due to their pro-angiogenic, anti-apoptotic, and immunomodulatory attributes. A variety of human tissues can be used as a source of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs), ranging from bone marrow (BM) to umbilical cord (UC). These cells are typically multipotent and can differentiate into
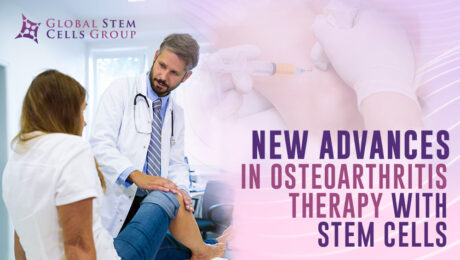
Osteoarthritis is a rheumatic pathology that damages the articular cartilage. By joining two bones through the joint capsule, the joints are able to move, providing us with functional autonomy. An inner fluid called synovial fluid is usually found within joints, which is produced by the synovial membrane. Articular cartilage covers the ends of the bones
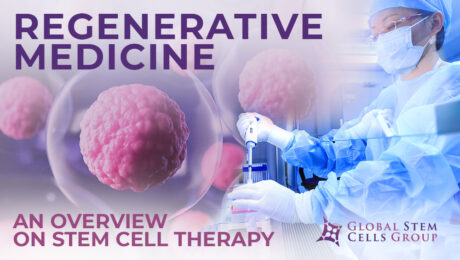
Stem cell therapy is a form of regenerative medicine designed to repair damaged cells within the body by reducing inflammation and modulating the immune system. This phenomenon makes stem cell therapy a viable treatment option for a variety of medical conditions. What is stem cell therapy? The term stem cell therapy refers to any treatment
Global Stem Cells Group has just announced the official opening of a new multi-specialty regenerative medicine center in Cancun. The new center is intended to incorporate different treatments based on regenerative medicine as well as to serve as a multi-specialty training center in the field of regenerative medicine and cellular therapies, offering doctors and patients
Recently, the Global Stem Cells Group announced plans to teach physicians the value and process behind incorporating regenerative medicine into their own clinical practices. MIAMI, 4–5 November 2022—Global Stem Cells Group, a multidisciplinary community of scientists and physicians that are working together to cure diseases and relieve human pain through the advancement of the field
With video lectures and additional tools from some of the most respected names in today’s stem cells field, the course arms practitioners with the necessary knowledge and resources to offer innovative regenerative medicine treatments in their existing practices. MIAMI, Florida— The International Society for Stem Cell Application (ISSCA) has announced it has launched a new